Art serves as a mirror to human culture, capturing the essence of our beliefs, values, and experiences. Among the myriad forms of art throughout history, “ancient art” stands out as a testament to our ancestors’ creativity and ingenuity. This article delves into the fascinating realm of ancient art, exploring its origins, styles, and significance in human history.
1. Introduction to Ancient Art
Ancient art encompasses the artistic creations of early human civilizations, spanning thousands of years and including a diverse array of mediums and styles. From early cave drawings to sophisticated sculptures in ancient Greece and Rome, ancient art offers a window into the lives and beliefs of our forebears.
2. The Origins of Ancient Art
The origins of ancient art can be traced back to prehistoric times when early humans began expressing themselves through drawings and carvings. These early forms of art were often created to communicate, tell stories, or convey religious beliefs. As civilizations evolved, so did their artistic practices, leading to the development of unique styles and techniques.
Prehistoric Art: The earliest known examples of ancient art are cave paintings found around the world, such as those in the Lascaux Caves in France and the Altamira Caves in Spain. Dating back over 30,000 years, these paintings depict animals, hunting scenes, and abstract symbols, reflecting the close relationship between early humans and their environment.
Evolution of Ancient Art: As societies transitioned from nomadic to settled lifestyles, new forms of artistic expression emerged, including pottery, sculpture, and architecture. These early works laid the foundation for the diverse and complex art forms that would later characterize ancient civilizations.
3. Styles in Ancient Art
Ancient art is marked by its diversity, with each civilization developing its own distinctive style. Here are some notable ancient art forms from various cultures:
Egyptian Art: Egyptian art is renowned for its unique style and symbolism, closely tied to religion and the afterlife. It often aimed to honor gods or ensure a deceased person’s safe passage to the afterlife.
- Hieroglyphics: A writing system using symbols and images.
- Sculptures and Statues: Depict gods, pharaohs, and other significant figures.
- Frescoes and Paintings: Found in tombs and temples, illustrating daily life, religious rituals, and the afterlife.
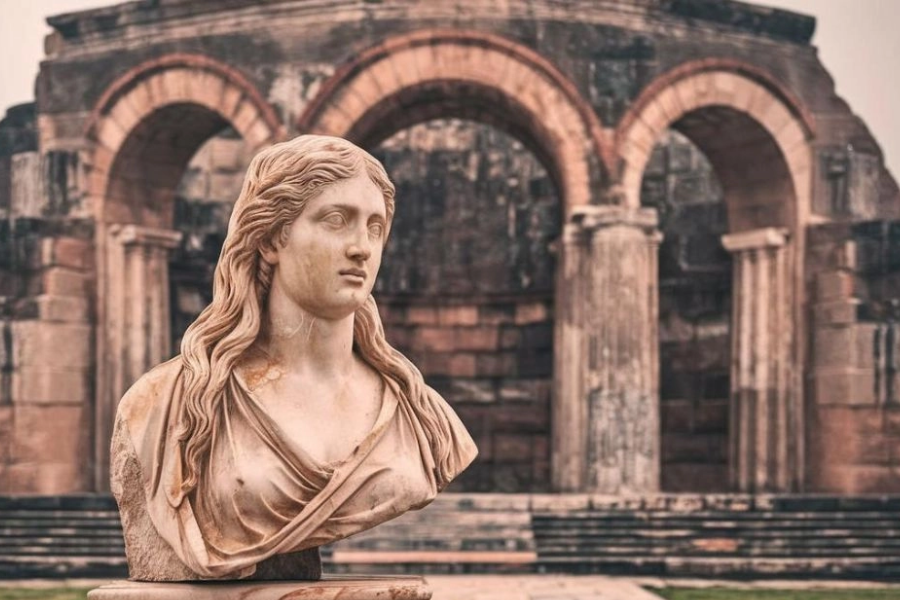
Greek and Roman Art: Greek and Roman art are deeply intertwined, with Roman art heavily influenced by Greek styles. These civilizations are celebrated for their achievements in sculpture, architecture, and pottery.
- Greek Art:
- Classical Sculptures: Emphasize idealized human forms and proportions.
- Pottery: Features vivid depictions of mythology and daily life.
- Architecture: Develops column orders (Doric, Ionic, Corinthian).
- Roman Art:
- Realism in Sculpture: Focuses on detailed and realistic portrayals of individuals.
- Mosaics: Intricate designs created from small pieces of stone or glass.
- Engineering and Architecture: Utilizes arches, domes, and concrete in grand constructions.
Chinese Art: Boasting one of the world’s longest continuous traditions, Chinese art emphasizes harmony, balance, and nature.
- Calligraphy: Regarded as the highest form of art, showcasing beautiful writing.
- Ink and Wash Painting: Simple, elegant depictions of landscapes, flowers, and birds.
- Ceramics: Famous for items like blue and white porcelain.
Indian Art: Deeply spiritual and religious, Indian art includes sculpture, painting, and architecture that reflect the subcontinent’s cultural and religious traditions.
- Sculpture: Depicts gods, goddesses, and mythological scenes.
- Temple Architecture: Known for elaborate and decorative carvings.
- Miniature Paintings: Small, detailed works often featuring court events or religious themes.
4. Materials and Techniques in Ancient Art
The materials and techniques used in ancient art varied widely based on the civilization and available resources. Here’s a summary of some key materials and methods:
| Civilization | Materials Used | Techniques Employed |
| Egypt | Stone, wood, gold, papyrus | Carving, painting, inlay, frescoes |
| Greece | Marble, bronze, clay | Sculpture, ceramics, fresco painting |
| China | Silk, ink, paper, porcelain | Calligraphy, painting, ceramics |
| India | Stone, wood, metal, textiles | Carving, painting, weaving, metallurgy |
| Rome | Marble, concrete, glass | Sculpture, mosaic, architecture |
These materials and techniques reflect both the resources available to these ancient civilizations and their cultural values and technological advancements.
5. Symbolism and Themes in Ancient Art
Ancient artists often used symbolism to convey deeper meanings. Common themes in ancient art include:
Religion & Spirituality: Many ancient artworks were created to honor deities or serve as offerings in religious rituals. Examples include Greek deity statues and Egyptian tomb frescoes.
Nature: Nature was a frequent theme, with artists drawing inspiration from the natural world. This is evident in Chinese landscape paintings and Native American ceramics featuring animal motifs.
Human Experience: Ancient art often depicted everyday life, such as farming, hunting, and social events, providing insight into past lifestyles.
Symbolism in Ancient Art:
- Chinese Art: The dragon (symbolizing power and strength) and the phoenix (symbolizing immortality).
- Egyptian Art: Symbols like the ankh (symbol of life) and the scarab beetle (symbol of rebirth).
- Greek Art: Mythological figures and symbols, such as the laurel wreath (symbolizing victory).
6. The Significance of Ancient Art in Modern Times
Ancient art continues to influence modern art and culture, inspiring artists, architects, and designers. Many contemporary artistic traditions build upon techniques and styles pioneered by ancient civilizations.
Influence in Modern Art:
- Reviving Classical Styles: The Renaissance saw a revival of Greek and Roman art, with artists like Michelangelo and Leonardo da Vinci drawing inspiration from ancient sculpture and architecture.
- Cultural Heritage: Ancient artifacts form a crucial part of many nations’ cultural heritage. Preservation and study of these works have renewed appreciation for early artistic achievements.
Ancient Art in Contemporary Design:
- Architecture: Modern buildings often incorporate elements of classical architecture, such as columns and arches.
- Fashion and Jewelry: Designers frequently draw on themes and styles from ancient Egypt, Greece, and Rome.
- Visual Arts: Contemporary artists continue to explore ancient art techniques and ideas, creating works that honor the past while pushing the boundaries of modern art.
7. Preservation of Ancient Art
Preserving ancient art is crucial for understanding our history and cultural heritage. Natural disasters, conflicts, and neglect have caused the loss or deterioration of many ancient artworks. However, ongoing preservation efforts help ensure that these works are appreciated by future generations.
Challenges of Preservation:
- Environmental Factors: Sunlight, moisture, and temperature fluctuations can damage ancient artworks.
- Human Impact: Looting, vandalism, and improper handling have led to the destruction of numerous artifacts.
- Technological Constraints: The preservation of ancient materials and techniques can be challenging with modern methods.
Efforts in Preservation:
- Restoration Projects: Organizations work to restore ancient artworks through repair and stabilization techniques.
- Museums and Exhibitions: Museums provide regulated environments to protect ancient artifacts from deterioration.
- Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of preserving ancient art is vital for ensuring its protection for future generations.
8. FAQs about Ancient Art
Q1: What is ancient art?
A: Ancient art refers to the artistic works of early human civilizations, including paintings, sculptures, pottery, and architecture, reflecting their cultural, religious, and social values.
Q2: What are some common materials used in ancient art?
A: Common materials include stone, wood, clay, metal, and textiles. The choice of materials often depended on the civilization’s resources.
Q3: How does ancient art differ from modern art?
A: Ancient art often focused on religious and mythical themes with strong symbolism, while modern art explores a broader range of themes, including abstract concepts and personal expression.
Q4: Why is it important to preserve ancient art?
A: Preserving ancient art is essential for understanding historical and cultural contexts and maintaining our shared cultural heritage.
Q5: How does ancient art influence modern art and design?
A: Ancient art inspires modern art and design through its techniques, styles, and themes, influencing contemporary architecture, fashion, jewelry, and visual arts.
9. Conclusion
Ancient art is a rich and diverse field that offers profound insights into the past, illuminating the creativity, beliefs, and experiences of early human civilizations. From prehistoric cave paintings to classical sculptures, these works continue to inspire and captivate us. By studying and preserving ancient art, we gain a deeper understanding of our history and the enduring power of artistic expression. Exploring the various forms, materials, and themes of ancient art allows us to appreciate our ancestors’ artistic achievements and recognize the lasting impact these works have had on shaping our world.
Discover expert insights and comprehensive guides on everything knots at Crock knot



Leave a Reply